1、数组的缺点
在其他语言中 数组的长度是固定的,所以数组被填满后在添加新的元素是非常困难的。在数组中添加和删除也是很麻烦的,需要把其他元素向前或者向后平移,以反映数组刚刚进行了添加或删除操作。
在JavaScript 中数组的主要问题是,它们被实现成了对象,与其他语言(比如 C++ 和 Java) 的数组相比,效率很低
2、 定义链表
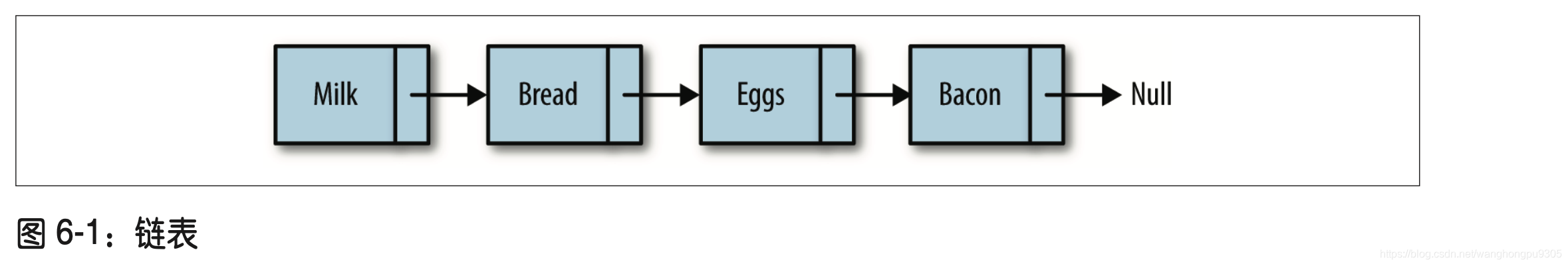
链表是由一组节点组成的集合,每个节点都使用一个对象的引用指向它的后继。指向另一 个节点的引用叫做链。
代码实现链表
// Node类用来表示节点
// element 用来保存节点上的数据,next用来保存指向下一个节点的链接
function Node(element){
this.element = element;
this.next = null ;
}
// LinkedList类 提供对链表进行操作的方法.
// 包含插入 删除节点 在列表中查找给定的值.该类也有一个构造函数,
// 链表只有 一个属性,那就是使用一个Node对象来保存该链表的头节点
function LList(){
this.head = new Node("head")
this.find = find
this.insert = insert;
this.findPrevious = findPrevious;
this.remove = remove;
this.display = display;
}
//head 节点的 next 属性被初始化为 null, 当有新元素插入时, next 会指向新的元素, 所以在这里我们没有修改 next 的值。
// 遍历链表,查找给定数据 并返回保存该数据的节点
function find(item){
var currNode = this.head;
while (currNode.element != item){
currNode = currNode.next
}
return currNode;
}
// find() 方法演示了如何在链表上进行移动。 首先, 创建一个新节点, 并将链表的头节点赋
// 给这个新创建的节点。 然后在链表上进行循环, 如果当前节点的 element 属性和我们要找
// 的信息不符, 就从当前节点移动到下一个节点。 如果查找成功, 该方法返回包含该数据的
// 节点; 否则, 返回 null。
// 一旦找到“后面” 的节点, 就可以将新节点插入链表了。 首先, 将新节点的 next 属性设
// 置为“后面” 节点的 next 属性对应的值。 然后设置“后面” 节点的 next 属性指向新节点。
// insert() 方法的定义如下
function insert (newElement,item) {
var newNode = new Node(newElement);
var current = this.find(item);
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
}
// display 用来显示链表中的元素
function display(){
var currNode = this.head;
while(!(currNode.next == null)){
console.log(currNode);
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
// 该方法先将列表的头节点赋给一个变量,然后循环遍历链表,当前节点的next属性为null时循环结束,为
// 了只显示包含数据的节点(换句话说,不显示头节点),程序只访问当前节点的下一个节点中保存的数据
// 从链表中删除一个节点时,需要先找到待删除节点前面的节点.找到这个节点后,修改它的next属性,
// 使其不再指向待删除节点,而是指向待删除节点的下一个节点.
// 先定义一个 findPrevious(), 遍历链表中的元素,检查每一个节点的下一个节点中是否存储着待删除的数据.
// 如果找到,返回该节点(即“前一个”节点),这样就可以修改它的next属性了,
function findPrevious(item) {
var currNode = this.head;
while(!(currNode.next == null) && (currNode.next.element != item)){
currNode = currNode.next
}
return currNode;
}
// 删除方法
function remove(item) {
var prevNode = this.findPrevious(item)
if(!(prevNode.next == null)) {
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
}
var cities = new LList();
cities.insert("Conway", "head");
cities.insert("Russellville", "Conway");
cities.insert("Carlisle", "Russellville");
cities.insert("Alma", "Carlisle");
cities.display();
console.log("------------------")
cities.remove("Carlisle");
cities.display();4 双向链表
//要为 Node 类增加一个 previous 属性
function Node(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.previous = null;
}
function LList() {
this.head = new Node("head");
this.find = find;
this.insert = insert;
this.display = display;
this.remove = remove;
this.findLast = findLast;
this.dispReverse = dispReverse;
}
//findLast() 方法找出了链表中的最后一个节点, 同时免除了从前往后遍历链表之苦:
function dispReverse() {
var currNode = this.head;
currNode = this.findLast();
while (!(currNode.previous == null)) {
// print(currNode.element);
console.log(currNode.element)
currNode = currNode.previous;
}
}
// findLast() 方法找出了链表中的最后一个节点, 同时免除了从前往后遍历链表之苦:
function findLast() {
var currNode = this.head;
while (!(currNode.next == null)) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
// 双向链表的 remove() 方法比单向链表的效率更高, 因为不需要再查找前驱节点了。 首先需
// 要在链表中找出存储待删除数据的节点, 然后设置该节点前驱的 next 属性, 使其指向待删
// 除节点的后继; 设置该节点后继的 previous 属性, 使其指向待删除节点的前驱。
function remove(item) {
var currNode = this.find(item);
if (!(currNode.next == null)) {
currNode.previous.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next.previous = currNode.previous;
currNode.next = null;
currNode.previous = null;
}
}
//findPrevious 没用了, 注释掉
/*function findPrevious(item) {
var currNode = this.head;
while (!(currNode.next == null) && (currNode.next.element != item)) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}*/
function display() {
var currNode = this.head;
while (!(currNode.next == null)) {
// print();
console.log(currNode.next.element)
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
function find(item) {
var currNode = this.head;
while (currNode.element != item) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
// 需要设置新节点的 previous 属性, 使其指向该节点的前驱。
function insert(newElement, item) {
var newNode = new Node(newElement);
var current = this.find(item);
newNode.next = current.next;
newNode.previous = current;
current.next = newNode;
}
var cities = new LList();
cities.insert("Conway", "head");
cities.insert("Russellville", "Conway");
cities.insert("Carlisle", "Russellville");
cities.insert("Alma", "Carlisle");
cities.display();
console.log("-----------------------")
cities.remove("Carlisle");
cities.display();
console.log("-----------------------")
cities.dispReverse();5 循环链表
如果你希望可以从后向前遍历链表, 但是又不想付出额外代价来创建一个双向链表, 那么就需要使用循环链表。 从循环链表的尾节点向后移动, 就等于从后向前遍历链表。
创建循环链表, 只需要修改 LList 类的构造函数:
function LList() {
this.head = new Node("head");
this.head.next = this.head;
this.find = find;
this.insert = insert;
this.display = display;
this.findPrevious = findPrevious;
this.remove = remove;
}
循环链表的 display() 方法如下所示:
function display() {
var currNode = this.head;
while (!(currNode.next == null) && !(currNode.next.element == "head")) {
console.log(currNode.next.element)
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
知道了怎么修改 display() 方法, 你应该会修改其他方法了吧? 这样就可以将一个标准的链表转换成一个循环链表了。